Table of contents
- What is Amazon EC2?
- Important terms related to Amazon EC2 Instance
- Step 1: Set up and log into your AWS account
- Step 2: Launch an Amazon EC2 instance in any region.
- Step 3: Configure your instance
- 1. Choosing Application and OS Images (AMI) Amazon Machine Image
- 2. Choosing Instance Type
- 3. Create key pair 🔑
- 4. Network settings
- 5. Configure storage
- 6. Advanced details
- 7. Reviewing Instance Launch
- 📌 To connect to your instance using the browser-based client from the Amazon EC2 console
- 🎉 Congratulations!
👋 Hello, everyone!
Let's start with Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2). You'll learn how to launch, connect to, and use a Linux instance. An instance is a virtual server in the AWS Cloud with Amazon EC2, you can set up and configure the operating system and applications that run on your instance. In this blog, you are learning how to create an EC2 instance with the help of the AWS management console.
What is Amazon EC2?

Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web service. It falls under the category of infrastructure as a service (IAAS). An AWS user can request and provision a compute server in the AWS cloud. that provides secure, resizable computing capacity in the cloud. It is designed to make web-scale cloud computing easier for developers. Amazon EC2's simple web service interface allows you to obtain and configure capacity with minimal friction.
It completely controls your computing resources and lets you run on Amazon’s proven computing environment. Amazon EC2 reduces the time required to obtain and boot new server instances (called Amazon EC2 instances) to minutes, allowing you to quickly scale up and down capacity as your computing requirements change. Amazon EC2 changes the economics of computing by allowing you to pay only for the capacity that you use. Amazon EC2 provides developers and system administrators the tools to build failure-resilient applications and isolate themselves from common failure scenarios.
Important terms related to Amazon EC2 Instance
Virtual computing environments, known as instances.
Preconfigured templates for your instances, known as Amazon Machine Images (AMIs), that package the bits you need for your server.
Various configurations of CPU, memory, storage, and networking capacity for your instances, known as instance types.
Secure login information for your instances using key pairs (AWS stores the public key, and you store the private key in a secure place).
Storage volumes for temporary data that are deleted when you stop, hibernate, or terminate your instance, known as instance store volumes.
Multiple physical locations for your resources, such as instances and Amazon EBS volumes, known as Regions and Availability Zones.
A firewall that enables you to specify the protocols, ports, and source IP ranges that can reach your instances using security groups.
Static IPv4 addresses for dynamic cloud computing, known as Elastic IP addresses.
Metadata, known as tags, that you can create and assign to your Amazon EC2 resources.
Virtual networks you can create that are logically isolated from the rest of the AWS Cloud and that you can optionally connect to your own network, known as virtual private clouds (VPCs).
You can launch a Linux instance using the AWS Management Console as described in the following procedure.
Step 1: Set up and log into your AWS account
Log into the AWS Management Console as the root account or IAM user.
Click on services --> compute --> EC2
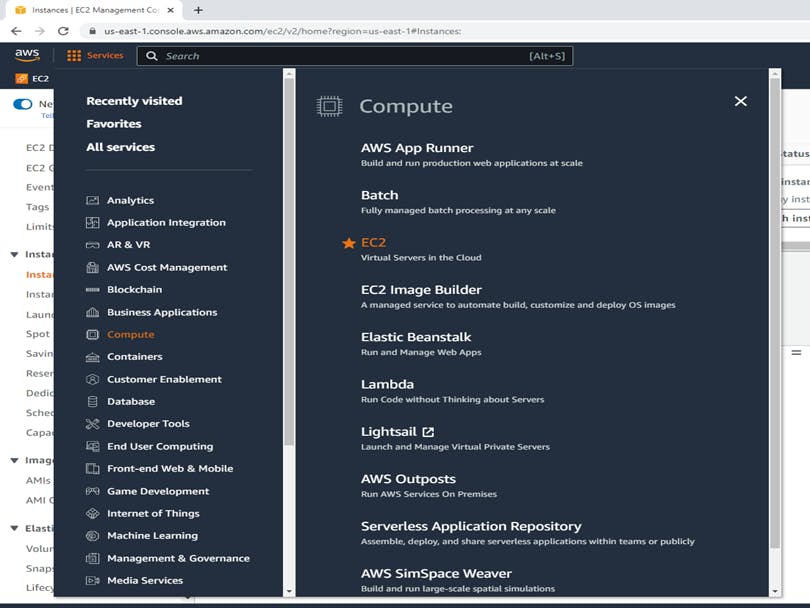
Step 2: Launch an Amazon EC2 instance in any region.
In the Amazon EC2 Dashboard, choose "Launch Instance" to create and configure your virtual machine. In the navigation bar at the top of the screen, the current Region will display. Here I have selected US East (N.Virginia)
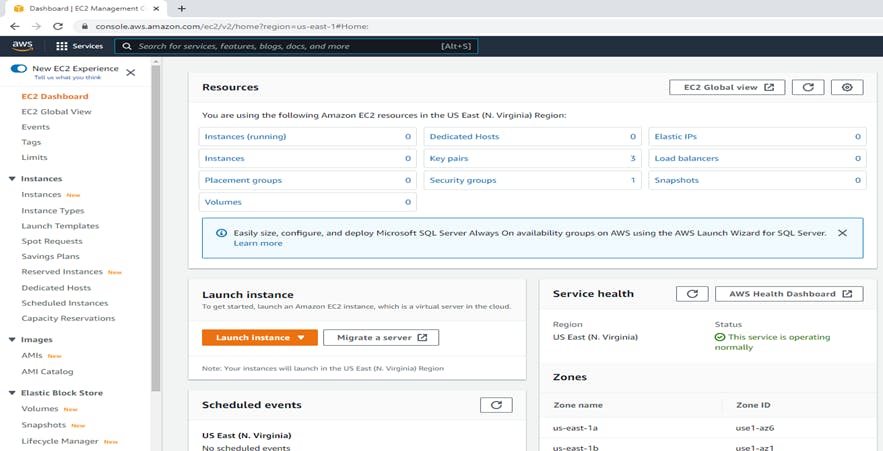
Step 3: Configure your instance
In the Launch an Instance wizard, Amazon EC2 allows you to create virtual machines or instances that run on the AWS cloud. So, we are giving the name "EC2-instance".

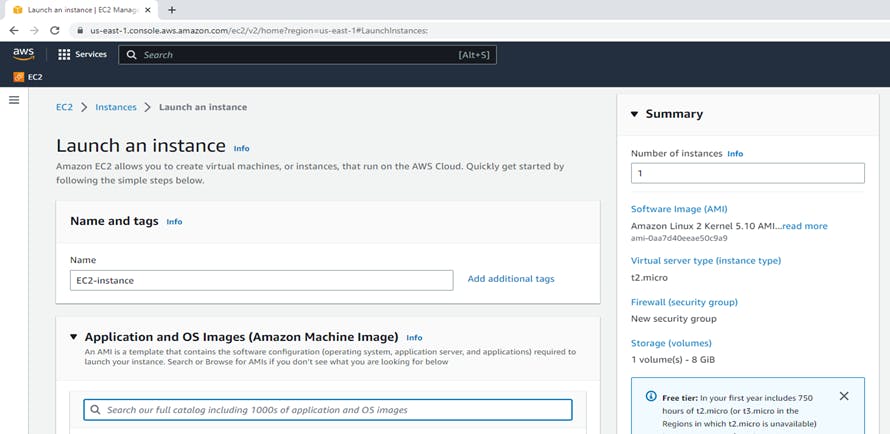
Process for launching an instance:
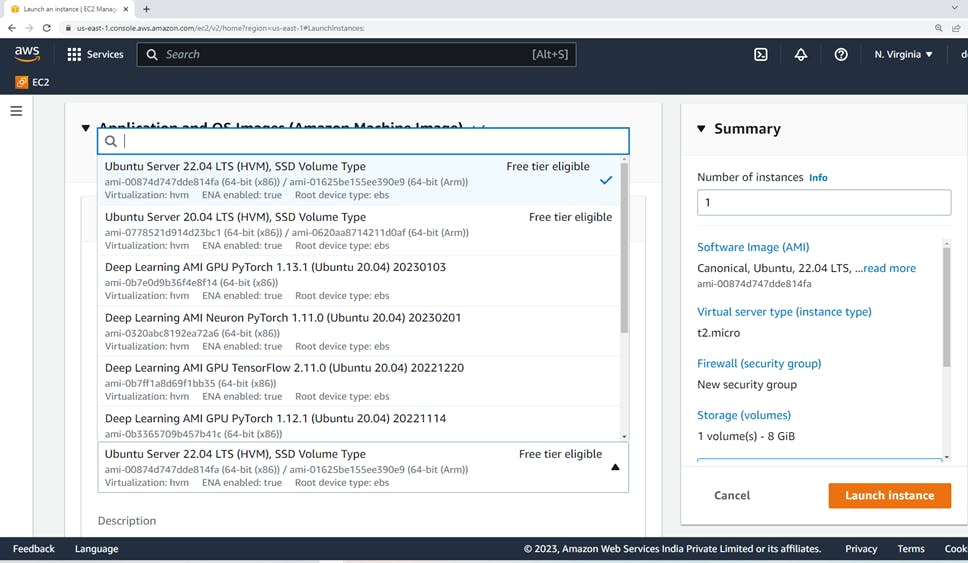
1. Choosing Application and OS Images (AMI) Amazon Machine Image
When you launch an instance, you must select a configuration, known as an Amazon Machine Image(AMI).
An AMI is a template that contains the software configuration (operating system, application server, and applications) required to launch your instance. You can select an AMI provided by AWS, our user community, or the AWS Marketplace; or you can select one of your own AMIs.
you can either select an AMI from the list, or you can select a Systems Manager parameter that points to an instance AMI ID.
On the Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) page, use one of two options to choose an AMI.
Either search the list of AMIs or search by the Systems Manager parameter.
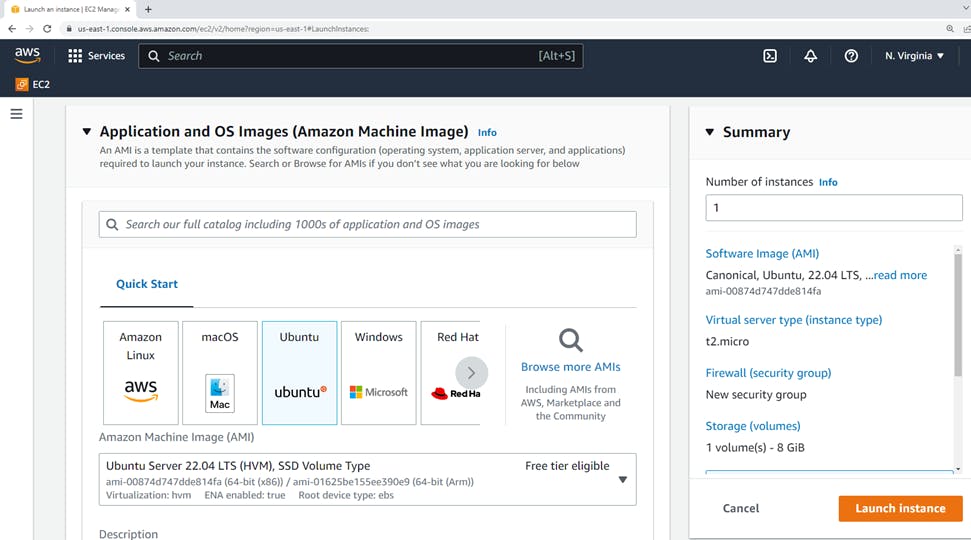
Here we have selected Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS(HVM). It is "Free tier eligible"
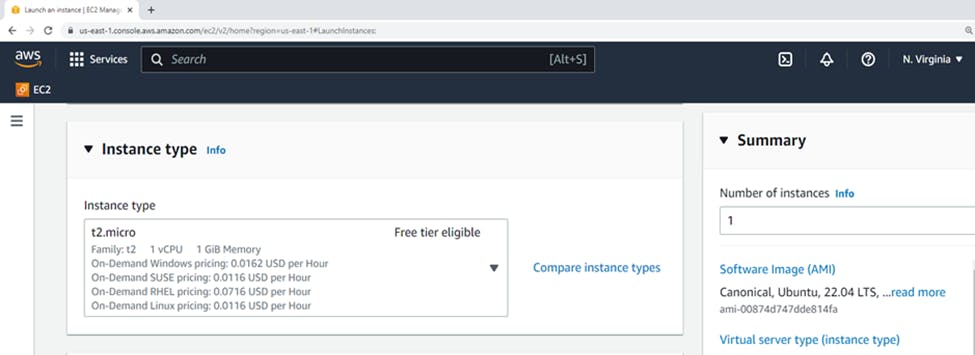
2. Choosing Instance Type
On the Choose an Instance Type page, select the hardware configuration and size of the instance to launch.
Larger instance types have more CPU and memory.
By default, the wizard displays current generation instance types and selects the first available instance type based on the AMI that you selected.
Choose an Instance Type page, you can select the hardware configuration of your instance. Select the t2.micro instance type, which is selected by default. The t2.micro instance type is eligible for the free tier. In some regions where t2.micro is unavailable, you can use a t3.micro instance under the free tier. For more information, see AWS Free Tier.
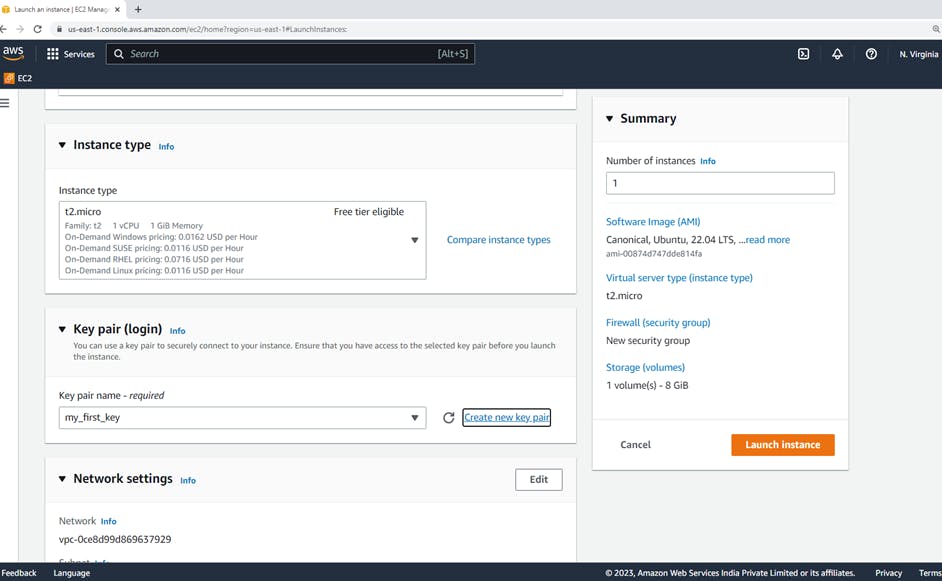
3. Create key pair 🔑
A key pair, consisting of a public key and a private key, is a set of security credentials that you use to prove your identity when connecting to an Amazon EC2 instance. Amazon EC2 stores the public key on your instance, and you store the private key.

so we have created the key pair "my_first_key.pem"
After creating a key pair make sure that u can save it properly for future reference.
4. Network settings
VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) – allows you to create a virtual network in AWS
Subnet in VPC (a key component in VPC)
Internet Gateway in VPC (allows communication between your VPC and the internet)
Route table (data file in RAM that is used to store route information about directly connected and remote networks)
Security group (acts as a virtual firewall)
Network ACL (an optional layer of security for your VPC)
Assign a security group – Select create a new security group.
Security group name – Name of the group. Ex: "my_cloud_devops"
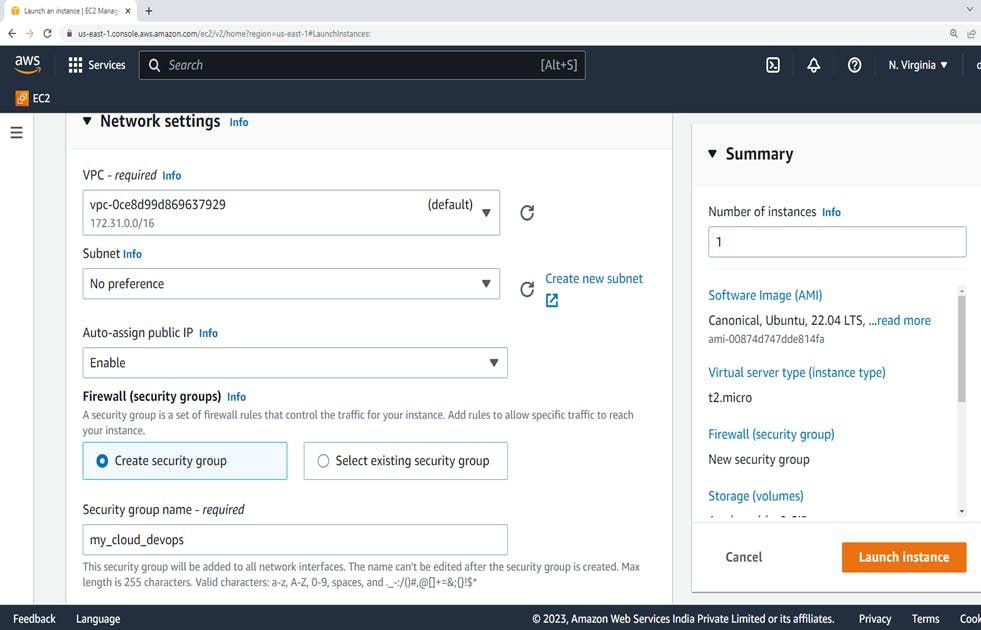
The security group name "my_cloud_devops"
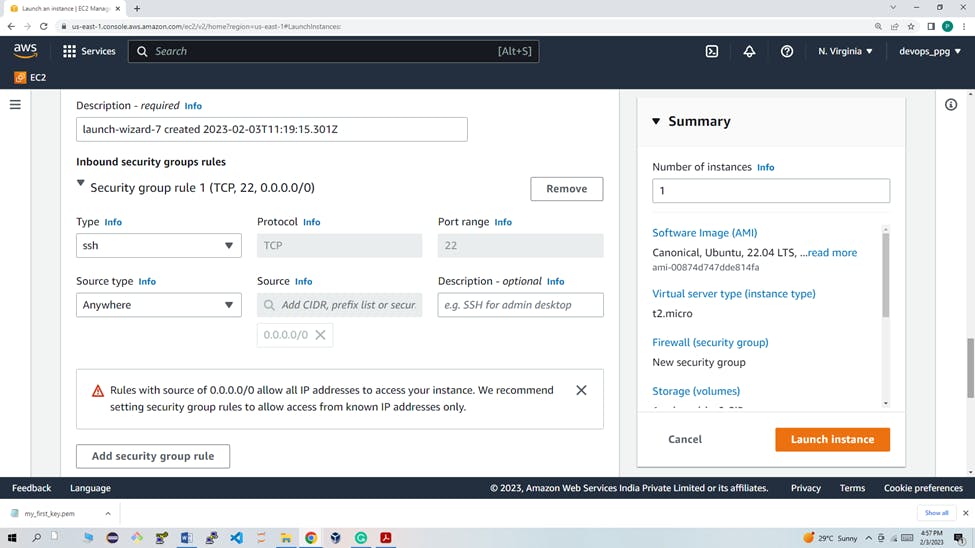
Set the rule for SSH, by selecting or setting the following values. They allow inbound SSH connections from all sources (any IP address).
Type: SSH, Protocol: TCP, Port Range:22, Source: Custom 0.0.0.0/0, Description: Accept SSH connections from all sources
if you want to add another rule use again source type. Create some rules that allow inbound HTTP and HTTPS connections from all sources. Click on Add Rule button.
Type: HTTP, Protocol: TCP, Port Range: 80, Source: Custom 0.0.0.0/0, Description: Accept unencrypted HTTP connections from all sources
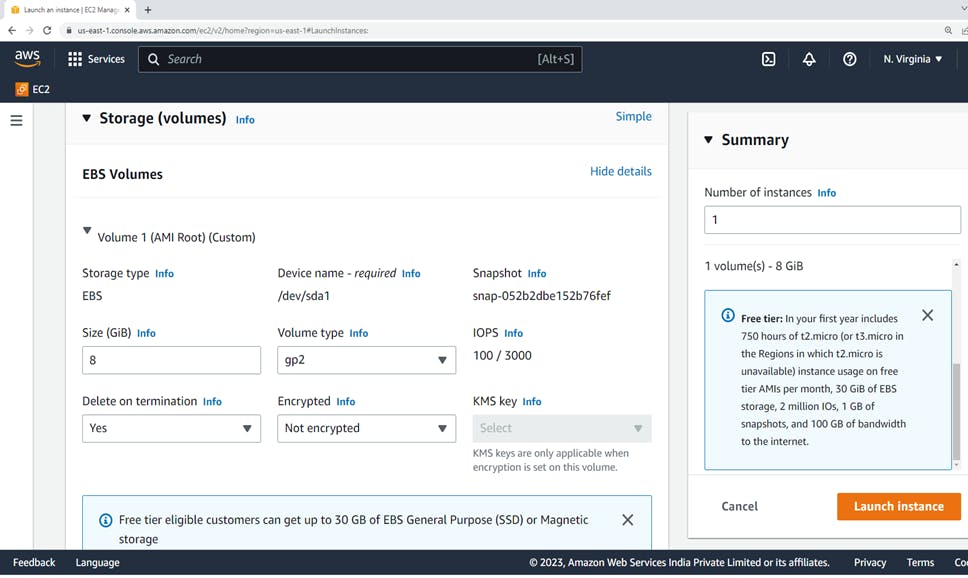
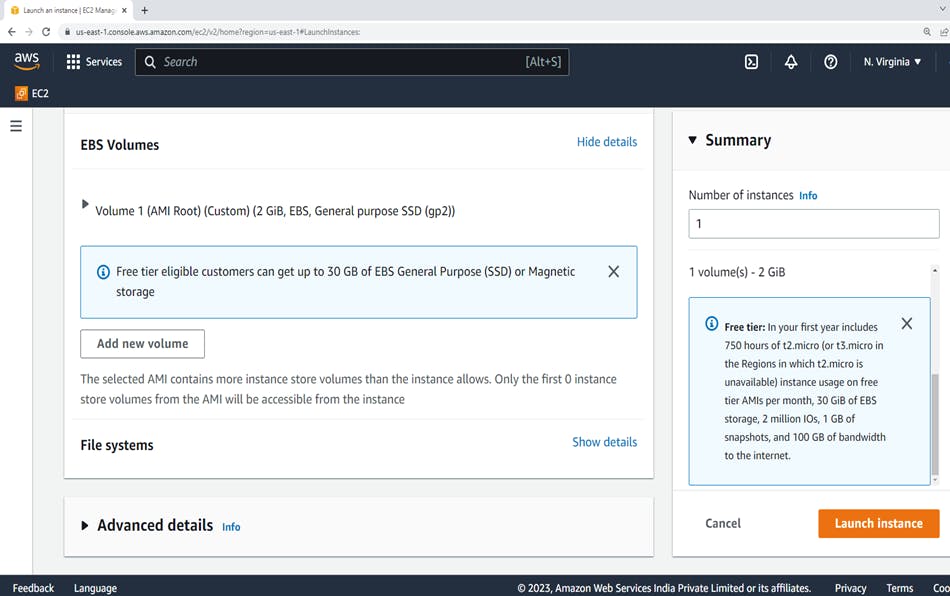
5. Configure storage
On the Configure storage, you can specify additional volumes to attach to the instance by choosing Add New Volume.
Configure each volume as follows.
Type: Select instance store or Amazon EBS volumes to associate with your instance.
Device: Select from the list of available device names for the volume.
Snapshot: Enter the name or ID of the snapshot from which to restore a volume.
Size: For EBS volumes, you can specify a storage size.
Volume Type: For EBS volumes, select a volume type.
IOPS: If you have selected a Provisioned IOPS SSD volume type. You can enter the number of I/O operations per second (IOPS) that the volume can support.
Delete on Termination: For Amazon EBS volumes, select this check box to delete the volume when the instance is terminated.
Encrypted: If the instance type supports EBS encryption, you can specify the encryption state of the volume.
6. Advanced details
The User data field is located in the Advanced details section of the launch instance wizard. Enter your shell script in the User data field.
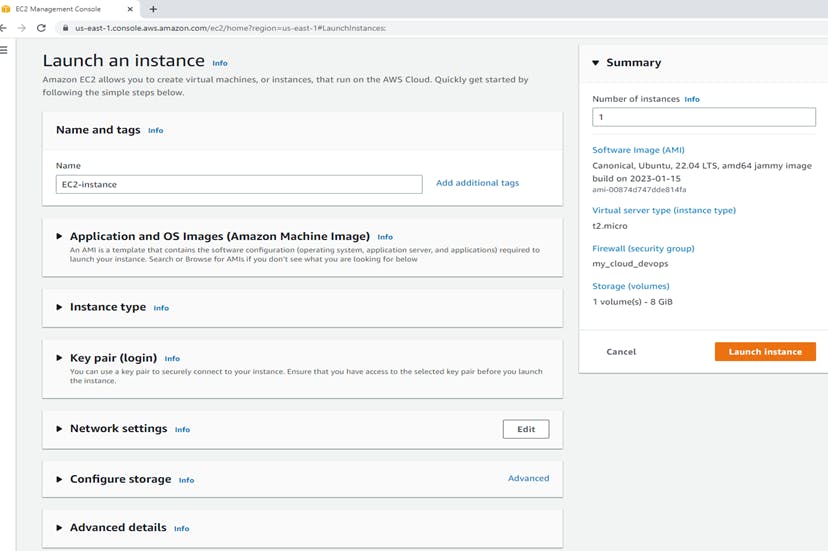
7. Reviewing Instance Launch
On the Instance Launch, check the details of your instance.
Then, make any necessary changes by choosing the appropriate Edit link.
Then, choose Launch.
To launch your instance, select the acknowledgment check box.
Finally, choose Launch Instances.
After you launch your instance, you can connect to it and use it. To begin, the instance state is
pending. When the instance state isrunning, the instance has started booting. There might be a short time before you can connect to the instance. We have successfully created an EC2 instance.
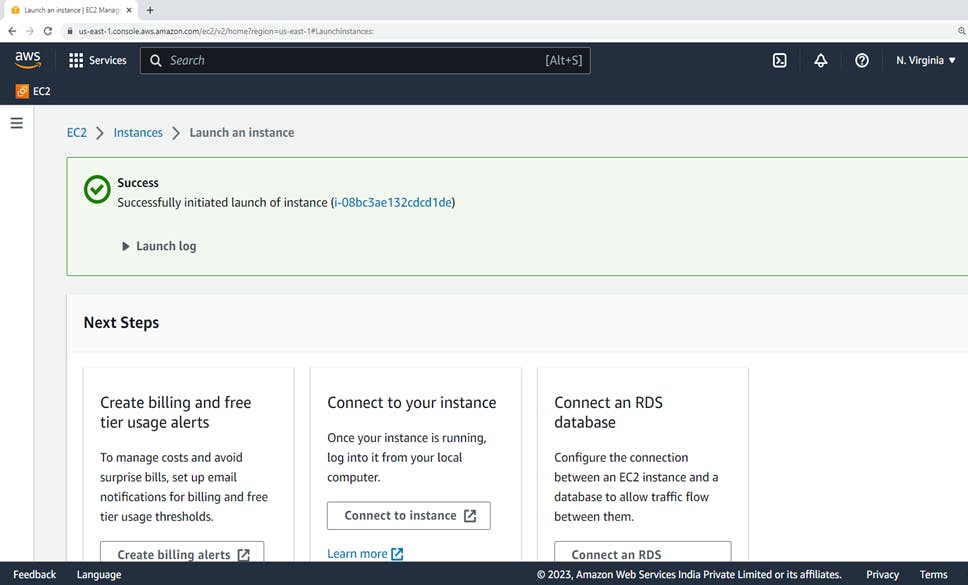
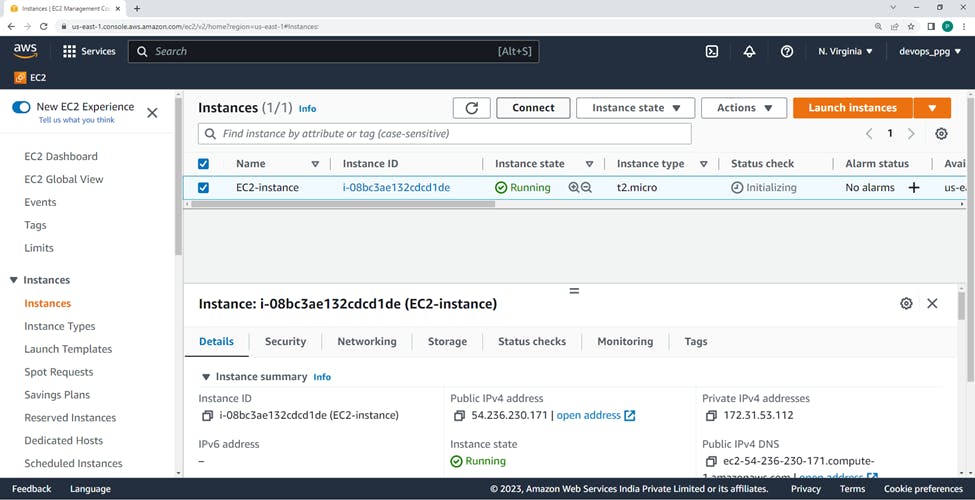
After successfully running the instance.
📌 To connect to your instance using the browser-based client from the Amazon EC2 console
In the navigation pane, choose Instances.
Select the instance and choose Connect.
Choose EC2 Instance Connect.
Verify the user name and choose Connect to open a terminal window.



If u don't need an instance you can stop Instance or Terminate the instance.
Pay-as-you-go cloud computing (PAYG cloud computing) is a payment method for cloud computing that charges based on usage.
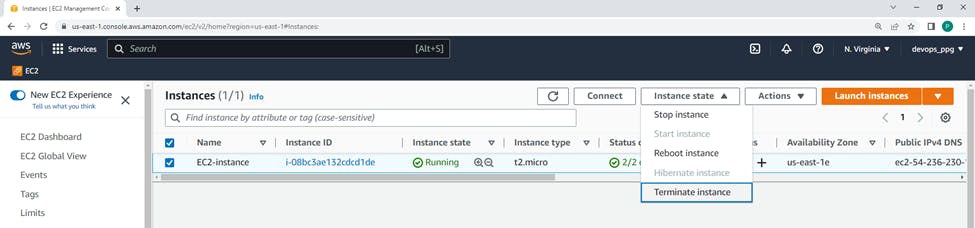
click on Terminate Instance --> dialog box will appear, to confirm that you want to terminate the instance.
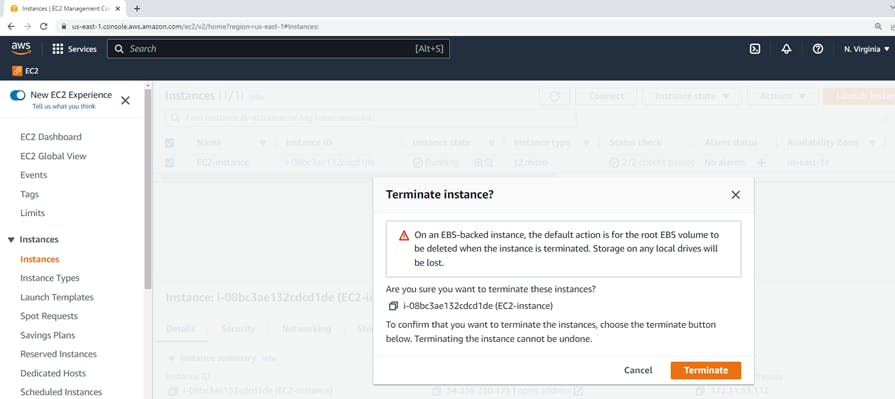
🎉 Congratulations!
You have learned how to create an EC2 instance and connect to an Instance. Terminate instance.
So it can be beneficial to do some research and find the opportunities that can be most helpful in building your career & becoming a part of the cloud computing world.
If you enjoyed this article, share it with your friends and colleagues!
